Tutorial
Microcontroller 8051 |
||||||
|
4.4. Send ADC
data to PC serially - RS 232
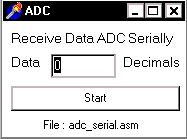
Figure 4.1. Sending ADC data serially to PC Step
1st Step
2nd org 0h
call initserial
;
start: mov a,p2; ambil data dari adc
call Sendout
sjmp start
;
Sendout:
detect: jnb ti,detect;
clr ti ;
mov sbuf,a ;
ret
;
initserial:
mov scon,#52h;initialize serial mode 1
mov tmod,#20h;timer1 mode 2
mov th1,#0F3h;Reload value for baud rate 2400
setb tr1
ret
end
To get the data from microcontroller serially, computer must run the program to get data from port communication RS232, in this experiment I have been used Delphi programming: ( Download Delphi File : adcserial.zip )
unit serial1; interface uses Windows, Messages, SysUtils, Classes, Graphics, Controls, Forms, Dialogs, ExtCtrls, StdCtrls; type
TForm1 = class(TForm)
Button1: TButton;
Timer1: TTimer;
Edit1: TEdit;
Label1: TLabel;
Label2: TLabel;
procedure Button1Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure Timer1Timer(Sender: TObject);
private
{ Private declarations }
public
{ Public declarations }
end;
var
Form1: TForm1;
data,status:byte;
const
base = $3f8;{base address port serial}
lcr = 3; {line control register}
dll = 0; {divisor lacht low byte}
dlh = 1; {divisor lacht high byte}
lsr = 5; {line status register}
implementation {$R *.DFM}
Procedure Initserial;
begin
asm
mov dx,base+lcr; {address line control register}
mov al,$80 ; {10000000b = access bit divisor lacht}
out dx,al
;
mov dx,base+dll; {address divisor lacht low byte}
mov al,$30 ; {DLLB = 30h}
out dx,al
;
mov dx,base+dlh; {address divisor lacht high byte}
mov al,$00 ; {DLLH = 00h}
out dx,al
; {Pada saat ini Port serial}
; {memp.baud rate = 2400 bps}
mov dx,base+lcr;{address line control register}
mov al,$03 ; {00000011b =}
out dx,al ; {bit 7=0, access to Rx buffer & Tx
; {bit 6=0, set break disable
; {bit 5-4-3=000, no parity
; {bit 2=0, one stop bit
; {bit 1-0=11,data lenght 8 bit}
end;
end;
Procedure Receive_Data_Serial; begin asm mov dx,base in al,dx mov data,al end end; procedure TForm1.Button1Click(Sender: TObject); begin initserial; timer1.enabled:=true; end; procedure TForm1.Timer1Timer(Sender: TObject);
begin
Repeat
asm
mov dx,base+lsr ; { address line status register }
in al,dx
and al,$01 ; {LSR = 00000001b, detects bit 0}
mov status,al ; {bit 0 = data ready}
end;
until status = $01;{ jika bit 0 = 1 then data ready}
Receive_Data_Serial;
edit1.text:=inttostr(data);
end;
end.
Step
3rd
|
Lesson 1: Lesson 2: |
|||||