| |
|
4.3. Taking data of DIP
Swicht serially.- Serial RS232
Communication standart using
serial data RS232 is very efective way to minimize cable connection.
This experiment, will be done by intake of data of DIP Swicht serially
with using serial data
communications RS232.
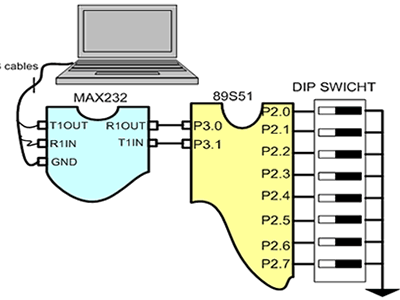
Figure 4.1. Sending data DIP swicht
serially to PC
Step
1st
Build the circuit as shown in figure 4.1. As you seen on figure 4.1.
Remember, that all we want to do with this lesson is take data DIP SW
trough PC serially.
Step
2nd
In this step, you must tipe the assembly program to make your serial
working, we assume that you have already known the editor, we used MIDE-51
to edit the program. ( Download File asm and
hex : dip_sw.zip,
Download File Complete Circuit File : SerialDipSW)
org 0h
nop
call initserial
gets: call inchar
mov P2,a
sjmp gets
;
initserial:
mov scon,#52h
mov tmod,#20h
mov th1,#-13
setb tr1
ret
;
inchar:
detect: jnb ri,detect;
clr ri
mov a,sbuf
ret
;
End
To get the data from microcontroller
serially, computer must run the program to get data from port communication
RS232, in this experiment I have been used Delphi programming: (
Download File Delphi : dipsw.zip )

(a)
(b)
Figure 4.2. Delphi Programming Display Data DIP SW
var
Form1: TForm1;
data,status:byte;
const
base = $3f8;{base address port serial}
lcr = 3; {line control register}
dll = 0; {divisor lacht low byte}
dlh = 1; {divisor lacht high byte}
lsr = 5; {line status register}
Procedure Initserial;
begin
asm
mov dx,base+lcr; {address line control register}
mov al,$80 ; {10000000b = access bit divisor lacht}
out dx,al
;
mov dx,base+dll; {address divisor lacht low byte}
mov al,$30 ; {DLLB = 30h}
out dx,al
;
mov dx,base+dlh; {address divisor lacht high byte}
mov al,$00 ; {DLLH = 00h}
out dx,al
; {In this case Port Serial have}
; { baud rate = 2400 bps}
mov dx,base+lcr;{address line control register}
mov al,$03 ; {00000011b =}
out dx,al ; {bit 7=0, access to Rx buffer & Tx
; {bit 6=0, set break disable
; {bit 5-4-3=000, no parity
; {bit 2=0, one stop bit
; {bit 1-0=11,data lenght 8 bit}
end;
end;
;
Procedure Receive_Data_Serial;
begin
asm
mov dx,base
in al,dx
mov data,al
end
end;
;
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
Initserial;
end;
procedure TForm1.Button1Click(Sender: TObject);
begin
initserial;
timer1.enabled:=true;
end;
procedure TForm1.Timer1Timer(Sender: TObject);
begin
Repeat
asm
mov dx,base+lsr; { address line status register }
in al,dx
and al,$01 ; {LSR = 00000001b, deteksi bit 0}
mov status,al ; {bit 0 = data ready}
end;
until status = $01 ;{ jika bit 0 = 1 then data ready}
Receive_Data_Serial;
edit1.text:=inttostr(data);
end;
Step
3rd
Safe your assembly program above, Compile the program that you have
been save by using MIDE-51, see the software instruction.
Step 4th
Download your hex file (dip_sw.hex ) into the microcontroller
by using Microcontroller ATMEL ISP software, see the instruction.After
download this hex file you'll see the action of serial transmition(
of course if your cable connection and your program are corrected ).
BACK
NEXT
|
|
Lesson 1:
T
o o l
1.1. Programmer
1.2. Edsim
51
1.3. MIDE-51
1.4. ATMEL
ISP
Lesson 2:
Input Output
2.1.LED
2.2.Swicht
2.3.7
Segmen
2.4.LCD
Character
2.5.ADC
2.6.DAC
2.7.Motor
Stepper
2.8.Keypad
Lesson 3:
Timer Counter
3.1.Basic
3.2.Mode
0
3.3.Mode
1
3.4.Mode
2
3.5.Mode
3
Lesson 4:
Serial Comm.
4.1.Basic
4.2.LED
4.3.Rotate
LED
4.2 ADC
4.3.LCD
Lesson 5:
Interuption
5.1.Basic
5.2.Timer
5.2.External
|


